Fake Fiction Text
Given nine different science fiction stories, one of which is fake and generated by AI, our goal is to use Voyant Tools to analyze the texts and identify the AI-generated story.
For Class: Tue Feb 11, 2025
| File | Text 1 | Text 2 | Text 3 | Text 4 | Text 5 | Text 6 | Text 7 | Text 8 | Text 9 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Drive | Drive | Drive | Drive | Drive | Drive | Drive | Drive. | Drive. | Drive |
Initial Hypothesis
At first, I suspected Text 3 to be the AI-generated story due to the unique occurrence of the word “Seaton”, which was not present in any of the other texts. This seemed abnormal at first glance. However, upon further consideration, I realized that “Seaton” is a proper name, and its uniqueness could be attributed to creative variation rather than artificial generation. This led me to adjust my approach to focus on broader linguistic patterns across all texts.
Refined Approach
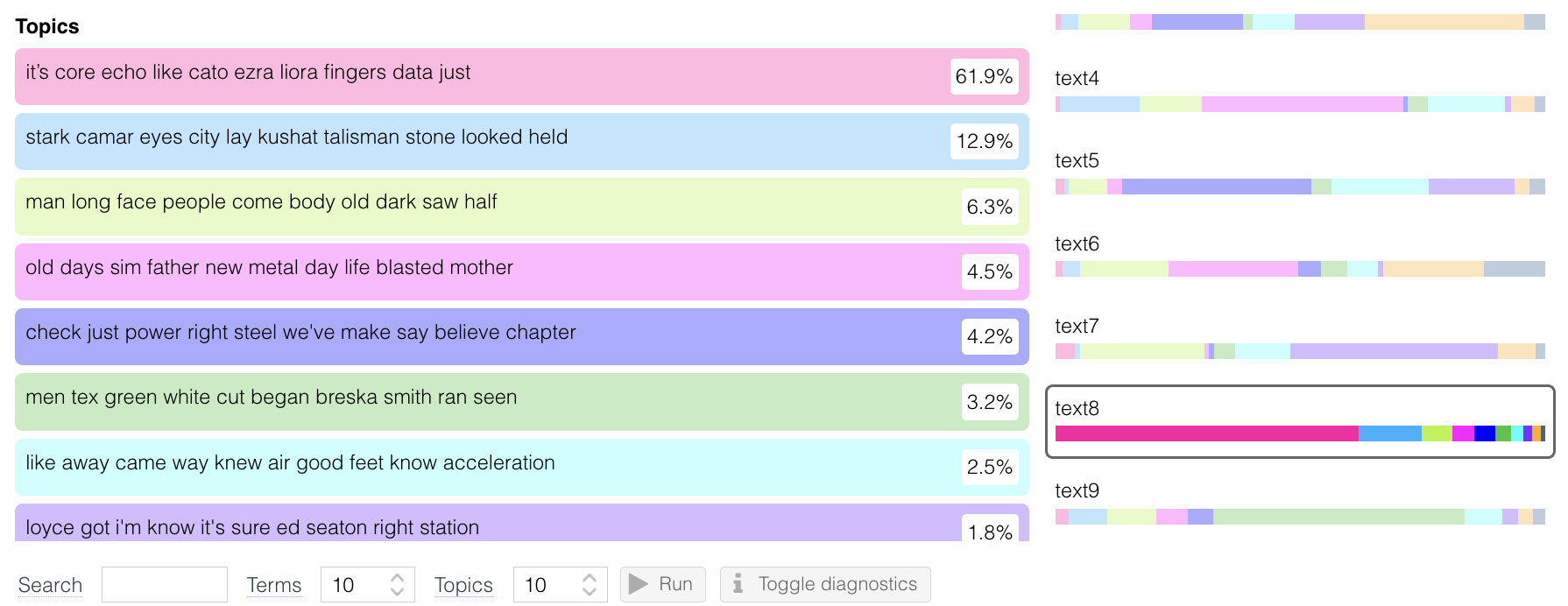
To identify the fake story, I analyzed the frequency of common words across all texts and compared patterns to uncover anomalies. The following key observations led me to suspect Text 8 as the AI-generated piece:

- Readability Score: Considering that AI-generated texts, particularly from models like GPT, often exhibit high readability, I assessed the readability levels across all texts. While this alone wasn’t conclusive, it helped narrow down the potential candidates to those with notably higher readability scores. Text 8 stood out in this regard.

- Topic Distribution: When comparing topic modeling results, I found that Text 8 exhibited an uneven topic distribution. One topic dominated with an extremely high percentage, while the other topics had significantly lower representation. In contrast, the other texts displayed a more balanced distribution across 3-4 topics, suggesting a more natural thematic spread typical of human writing.
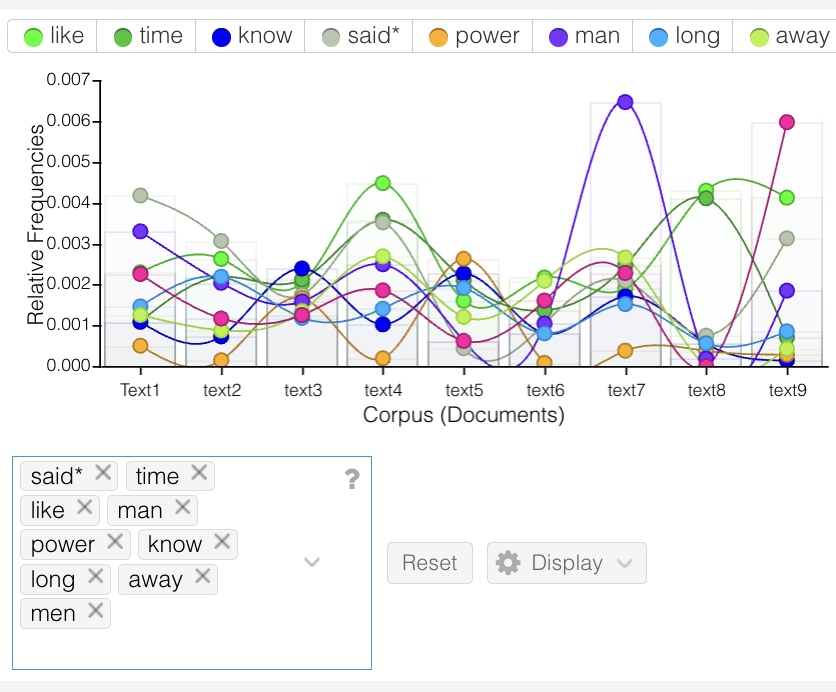
- Relative Frequency of Common Words: Examining the relative frequency of common words revealed abnormalities in both Text 3 and Text 8. Text 3 showed an unusually consistent frequency for all common words, almost as if it were deliberately controlled. Similarly, Text 8 displayed controlled frequency patterns, though split across two distinct frequency ranges. This level of regularity is often characteristic of AI-generated text.
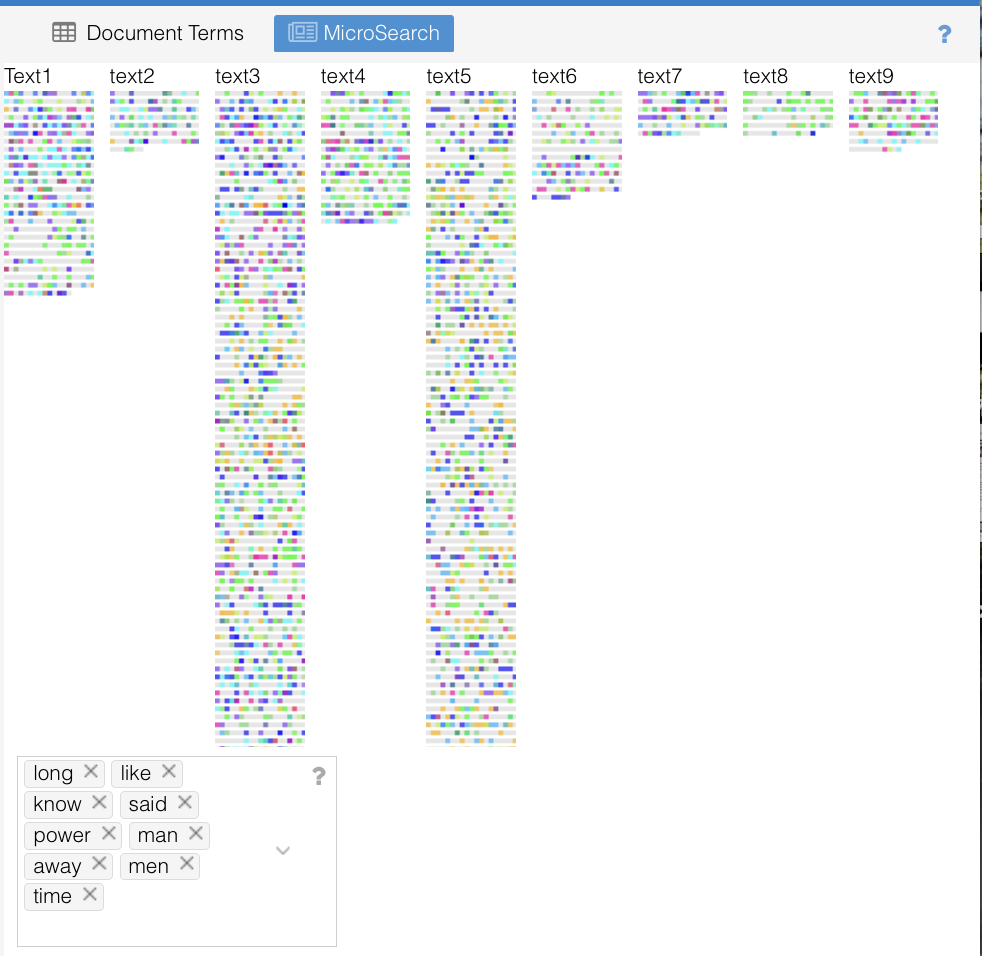
- Micro Search: Analyzing the distribution of frequent words throughout the texts, I observed that Text 8 was less “colorful,” exhibiting a limited variety and usage of these words. This lack of lexical diversity suggests a mechanical generation process, as AI models may struggle to replicate the nuanced word choices typical of human authors.
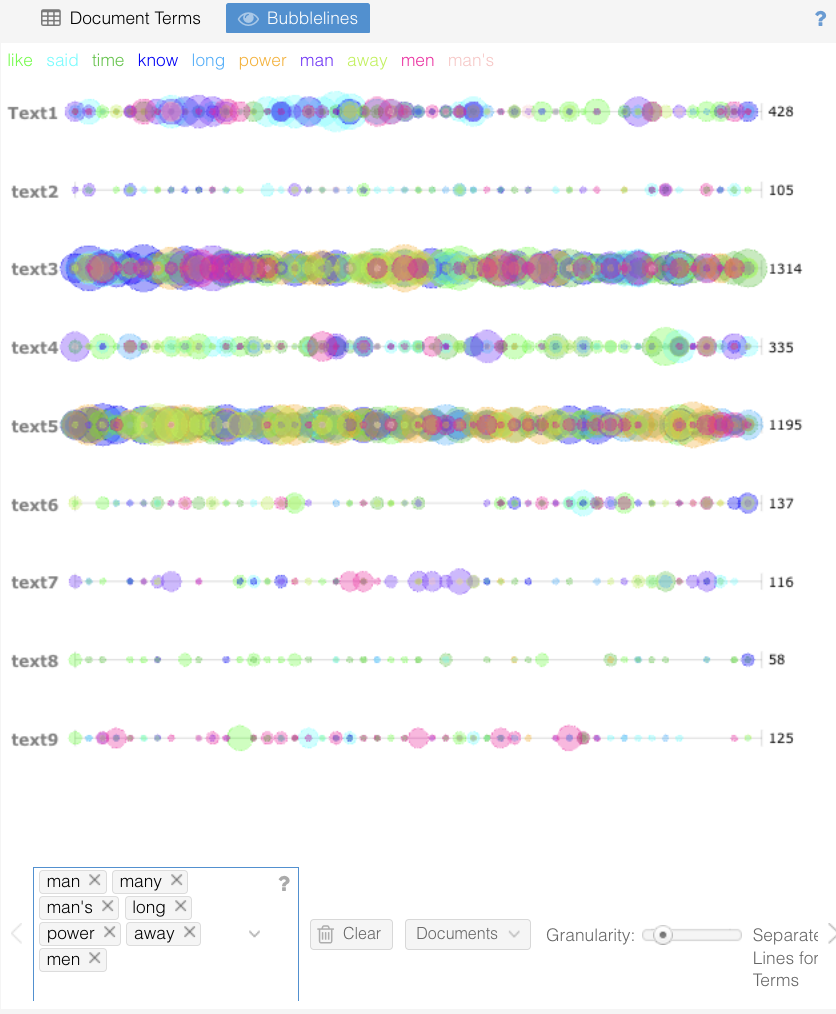
- Bubblelines Visualization: In the Bubblelines visualization, both Text 2 and Text 8 demonstrated evenly spaced and balanced patterns in the occurrence of common words—patterns that appeared almost machine-like in their precision. While this raised suspicion for both texts, the consistency observed in Text 8 aligned with other anomalies I had identified.
- Mandala Visualization (Keyword Usage): Through the Mandala visualization, I noticed that Text 8 did not contain the words “men” and “away”, both of which appeared in all the other texts. The absence of these common words in Text 8 further highlighted its deviation from typical human writing patterns.
| Mandala “Men” | Mandala “Away” |
|---|---|
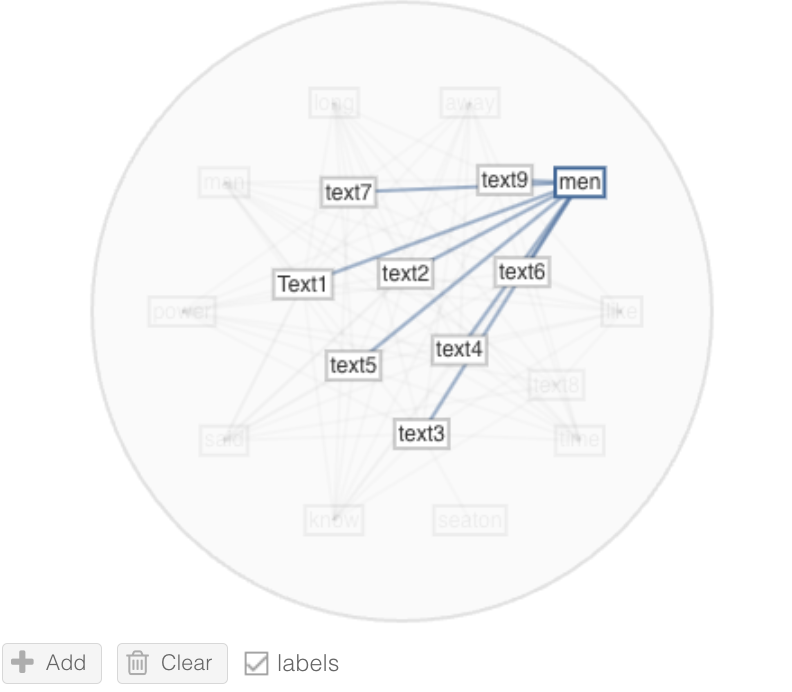 |
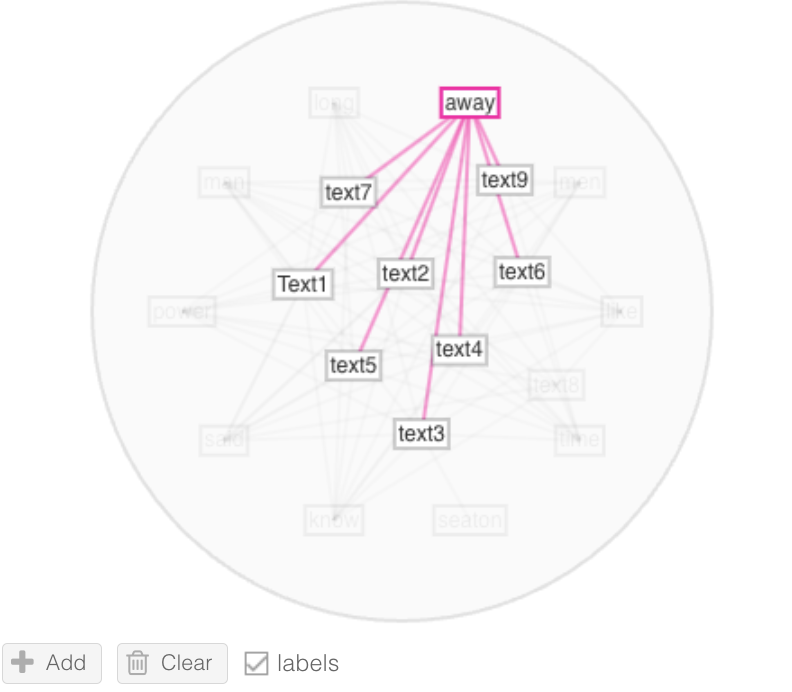 |
Conclusion
Considering all these uncommon patterns—high readability, uneven topic distribution, controlled word frequency, limited lexical richness, machine-like bubbleline patterns, and missing common keywords—I concluded that Text 8 is most likely the AI-generated story.
✅ Ready for grading